Digital Training: The Approach For Generation Z

Digital Training: The Approach For Generation Z
Lack of interaction. Unsociable. Can’t hold a conversation. There is a common belief that Generation Z (those born between 1997 and 2012) hold many of these traits, but recent research is challenging these stereotypes. In fact, a study by Bridgeworks found that 40% of Generation Z employees want daily interactions with their boss, which is good news for safety managers who are experienced with face-to-face communication. When these interactions do not occur, workers sometimes believe that they must have done something wrong. Facilitating in-person connections can prove advantageous for safety managers, helping them build solid relationships with their employees.
Furthermore, Generation Z places significant importance on learning on the job. A study of 5,000 high school students indicated that young people in the US are moving away from the traditional route of undertaking a four-year college degree before beginning to work. Instead, they are opting for a shorter period of formal education and then relying on on-the-job training. Findings show that nearly one third of teens prefer two years or less of education post-high school, while more than half are open to something other than a four-year college education.
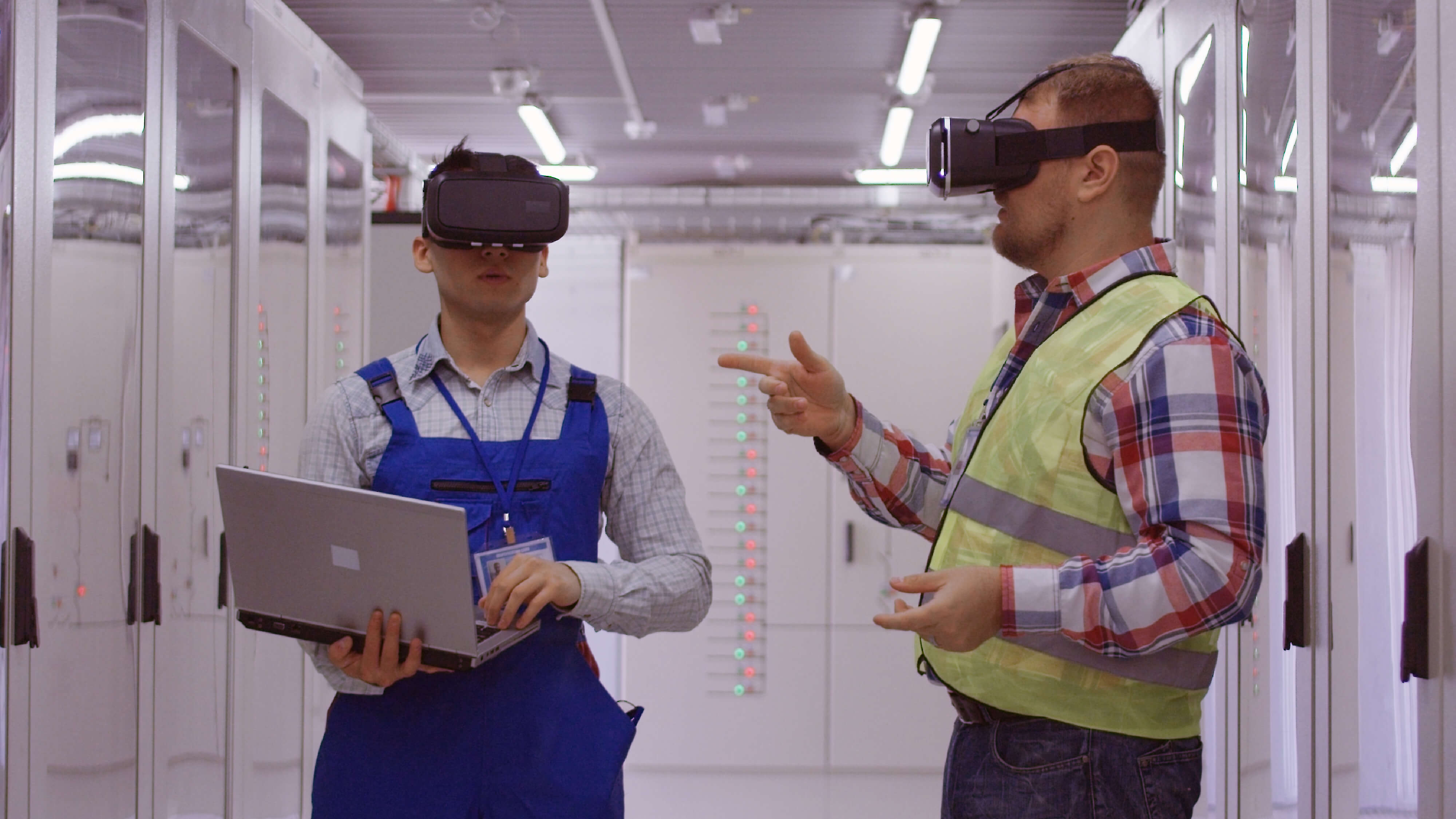
With these preferences in mind, emerging technology presents a viable solution to facilitate efficient on-the-job training. Technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) can provide an interactive experience, which is perceived as the preferred route for Generation Z, rather than classroom learning. A Barnes & Noble College study indicated that 51% of Gen Z students learnt best by working through examples, 38% preferred visual media, and a mere 12% favoured the lecture approach. AR and VR can facilitate preferred methods of workplace learning, as workers can practise their job's various tasks, gaining confidence and competency before stepping onto a worksite. Higher worker competency reduces the likelihood of serious injuries and fatalities, a major priority for EHS functions in the upcoming year.
Although these emerging technologies are exciting, they must overcome challenges associated with cost, ergonomics and internet bandwidth before being adopted widely. Nonetheless, there are cheaper training tools that leverage commonplace technology. In a survey by Kahoot, 65% of Gen Z respondents said that they would like to see mobile apps as a training tool in the workplace. The EHS software market has taken notice of these trends. Our latest Green Quadrant report revealed that all 23 software vendors have mobile apps, with some offering microlearning tools as part of their training platform. Unlike classroom learning, which requires workers to be present, mobile apps can be accessed from remote locations and telecommuting settings. As workers are encouraged to access these apps regularly, training becomes an ongoing process, and employees are constantly improving their safety knowledge in conjunction with increasing regulation.
In 2020, Generation Z made up 20% of the UK workforce. As a group that has been exposed to technology from a young age, it is likely that their preference for digital learning tools will only grow. New technology platforms such as the metaverse, which has been cited as an appropriate path for digital EHS training, could enhance the interactive learning experience even further.