Five GenAI-Enabled Low-Code Industrial Analytics Use Cases Firms Can Get Started With Today

Joe Lamming
Generative AI is bigger than ever. Tech multinationals, start-ups, their investors, analysts, regulators and media pundits haven’t yet taken their foot off the accelerator in developing larger models, trained on more multimodal data, with more sophisticated scaffolding. Despite a report by Goldman Sachs published at the end of June titled “GEN AI: TOO MUCH SPEND, TOO LITTLE BENEFIT?” – where they estimated a total of “over $1tn on AI capex in the coming years” – enterprises and industrial firms large and small continue to experiment internally and trial external commercial AI-enabled solutions. On July 23rd, Meta released its Llama 3.1 family of open-weight models, including a 405-billion parameter behemoth surpassing performance benchmarks of the best closed models like OpenAI’s GPT-4o.
The truth is, the most promising applications of large AI models change radically depending on the user’s perspective. For software engineers, LLMs have long since fundamentally changed how code is written, debugged and improved upon. For data entry professionals, daily tasks have largely evolved beyond robotic drudgery and towards supervision of automated data scrapers and bizarre edge case resolution. Knowledge workers, such as those writing blogs like this, are still largely holding their breath – but are keenly aware of information management capabilities on the horizon.
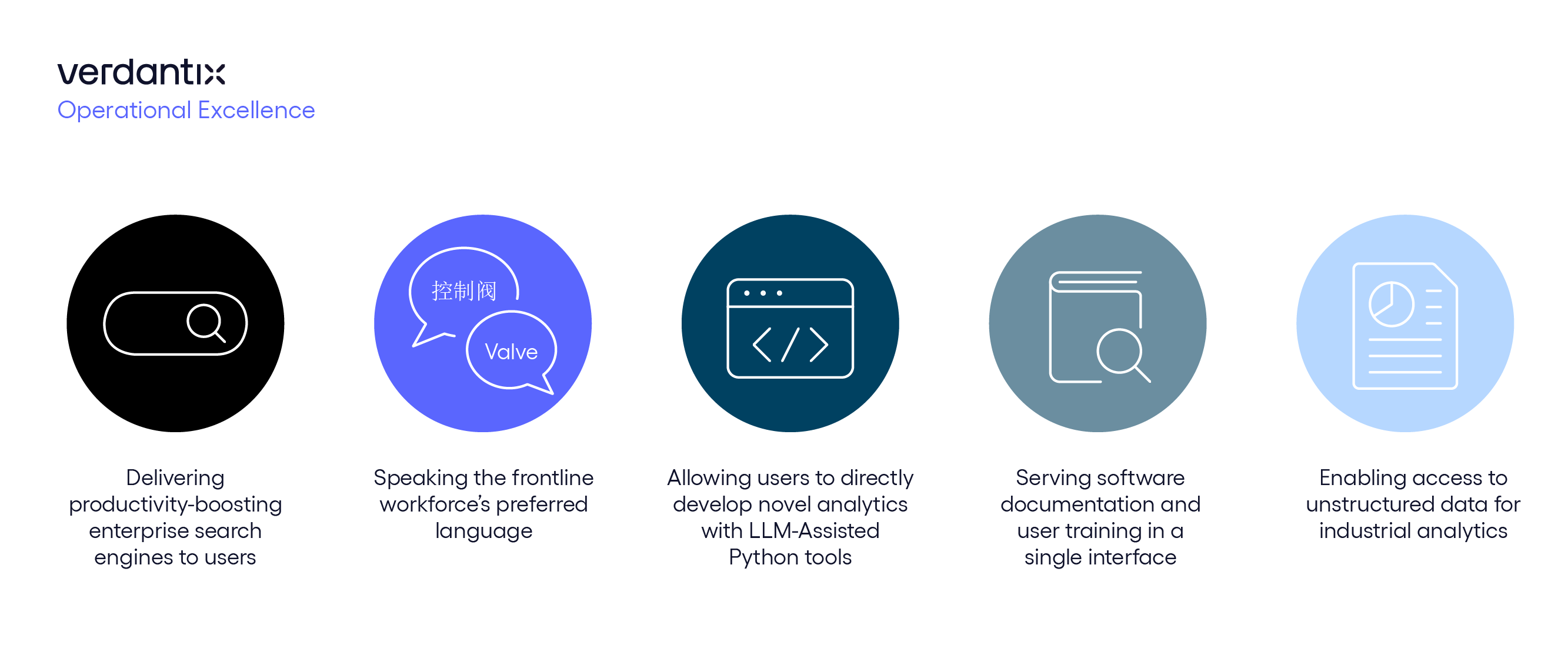
Five use cases for GenAI-driven low-code/no-code (LCNC) industrial analytics software solutions are gaining traction amongst end users. These include:
- Delivering productivity-boosting enterprise search engines to users.
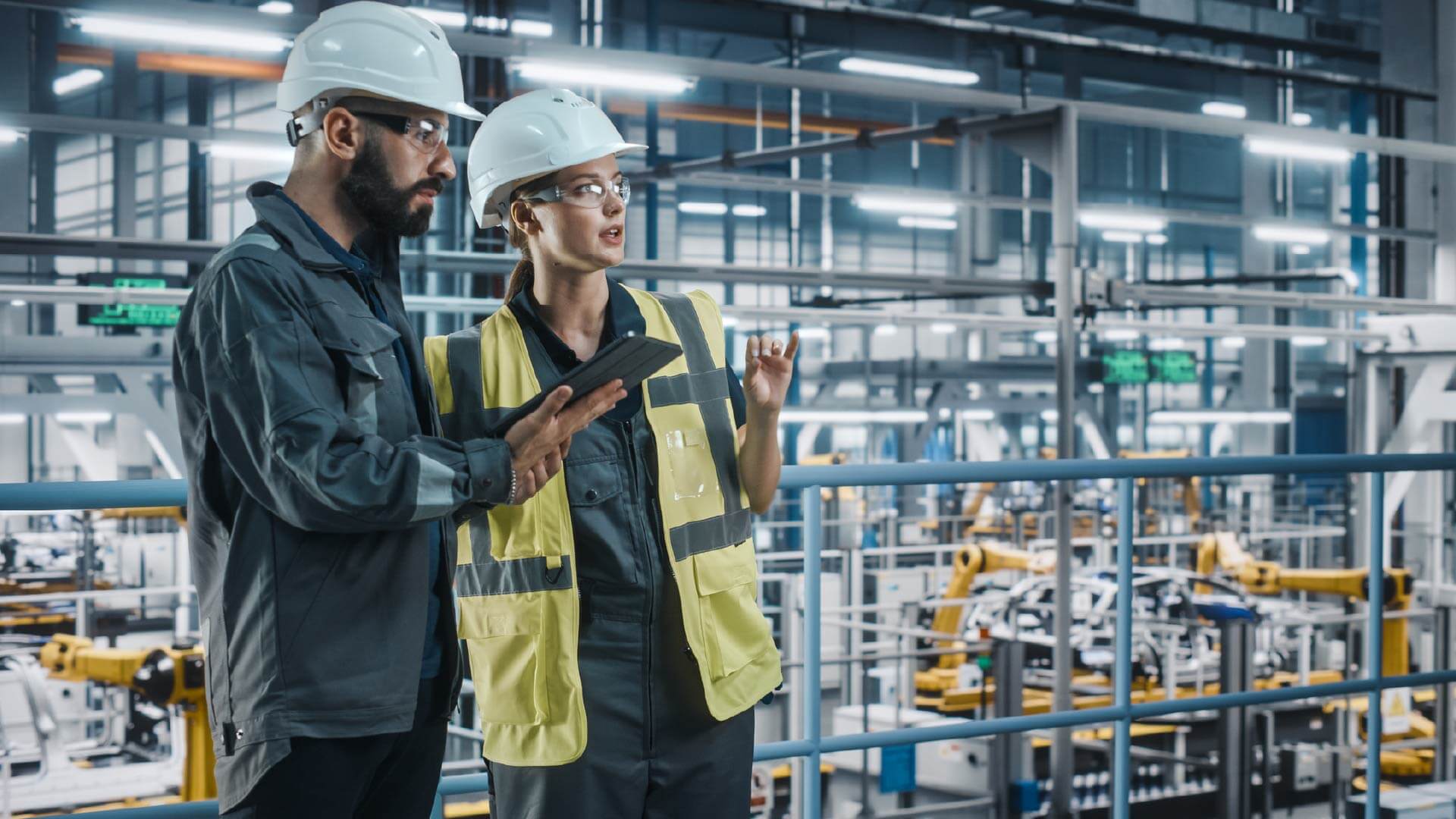
The search bar UI element has long endured. Users avoiding folder navigation will instead type the tag name and rely on their software to interpret this query and surface relevant information. LLMs were introduced by Google from 2019 to enable semantically similar results in its Search product, while Perplexity and Microsoft’s Bing popularized GenAI search in early 2023. Industrial software vendors quickly followed, with C3 AI, Cognite and Palantir offering AI-driven search tools, enabling rapid, robust, natural-language-focused LCNC data retrieval alongside richly visual, drill-down GUIs to see information and sources in context, to aid decision-making.
- Speaking the frontline workforce’s preferred language.
An original use case of the Transformer architecture behind many of today’s GenAI tools is its ability to translate language, and therefore reduce communication barriers. Today’s frontier models, such as Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Meta’s Llama 3.1 405B, can understand and generate responses in most human languages, while OpenAI is finally rolling out bidirectional, low-latency audio communication with GPT-4o, albeit with unexpected results. Multilingual, multimodal communication is crucial in global industrial operations – by facilitating communication in the preferred languages of the workforce, frontline workers and managers can focus on engineering and process safety, not IT.
- Allowing users to directly develop novel analytics with LLM-assisted Python tools.
GenAI is democratizing data science by enabling domain experts with minimal coding knowledge to develop sophisticated analytics solutions. Seeq’s AI Assistant uses LLMs to assist users in generating Python code for data analytics directly from natural language descriptions of goals. This, too, flattens the learning curve to get those most familiar with industrial operations into the analytics seat to make better-informed decisions.
- Serving software documentation and user training in a single interface.
Complex software requires complex documentation, slowing down the learning process. GenAI simplifies this by providing a single, intelligent interface that users can query to get specific, contextually relevant information, streamlining on-the-job training and boosting problem-solving by delivering precise guidance based on vast repositories of documentation, tailored to only the most immediate tasks. ERP behemoth SAP introduced its Joule assistant in September 2023 to deliver context-dependent guidance on tools, while AWS made its Amazon Q in-context documentation assistant generally available in April 2024.
- Enabling access to unstructured data for industrial analytics.
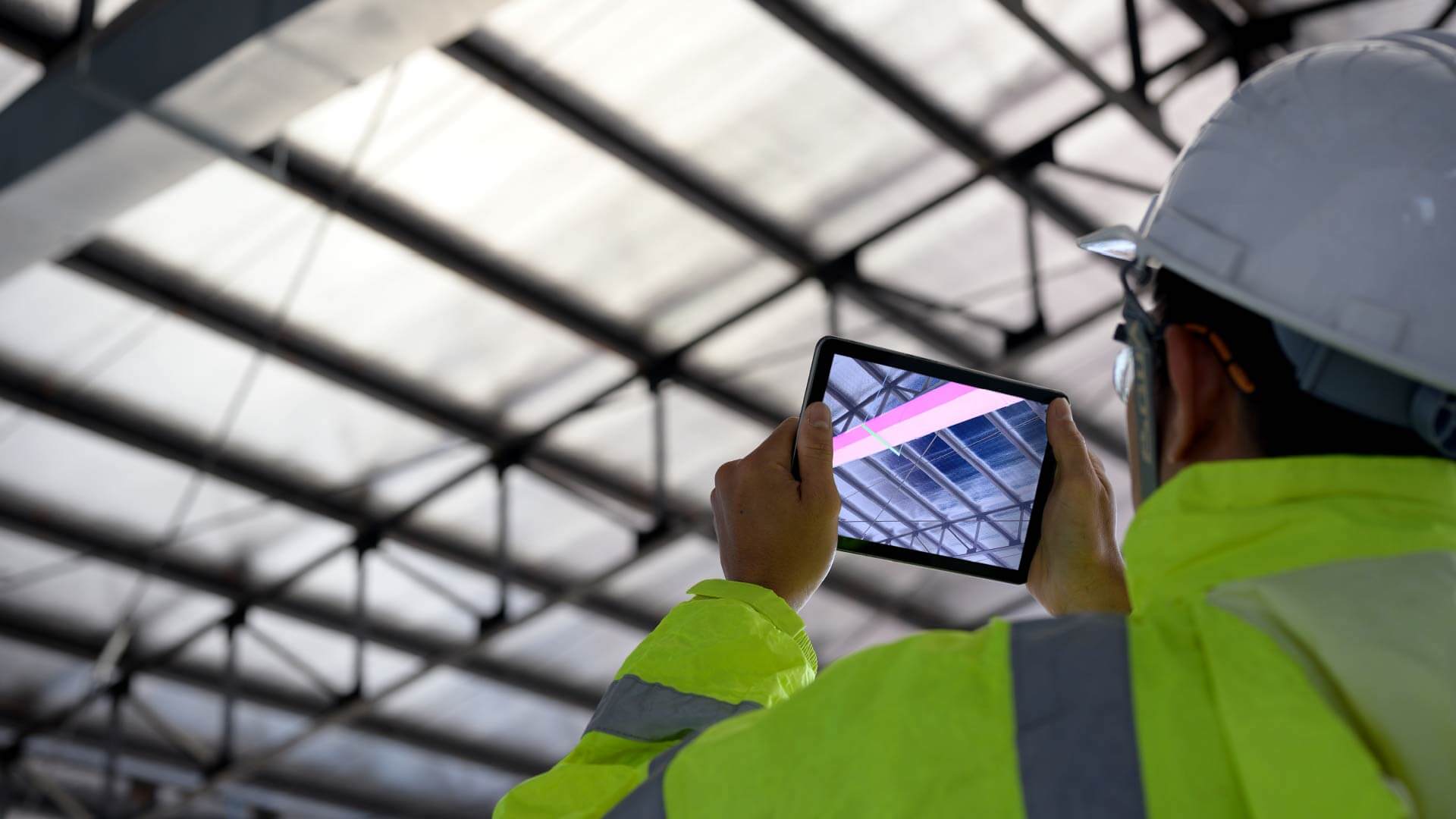
All industrial data begins unstructured, often staying unstructured – locked in PDFs, images and handwritten notes that traditional analytics tools cannot directly interpret. LLMs excel in structuring this unstructured data, extracting valuable information that can be integrated into operational workflows. C3 AI worked with a large agricultural firm to tune its C3 Generative AI solution and PDF table extraction libraries from an out-of-the-box baseline retrieval accuracy of 12% to a level of 88% within four weeks.
Check out our related research: Strategic Focus: Low-Code Industrial Analytics Enabled By Generative AI, Market Insight: Practical High-Value Industrial Use Cases For Generative AI In 2024.
About The Author

Joe Lamming
Senior Analyst