Game-Changing PFAS Regulations: Navigating New Federal And State Rules
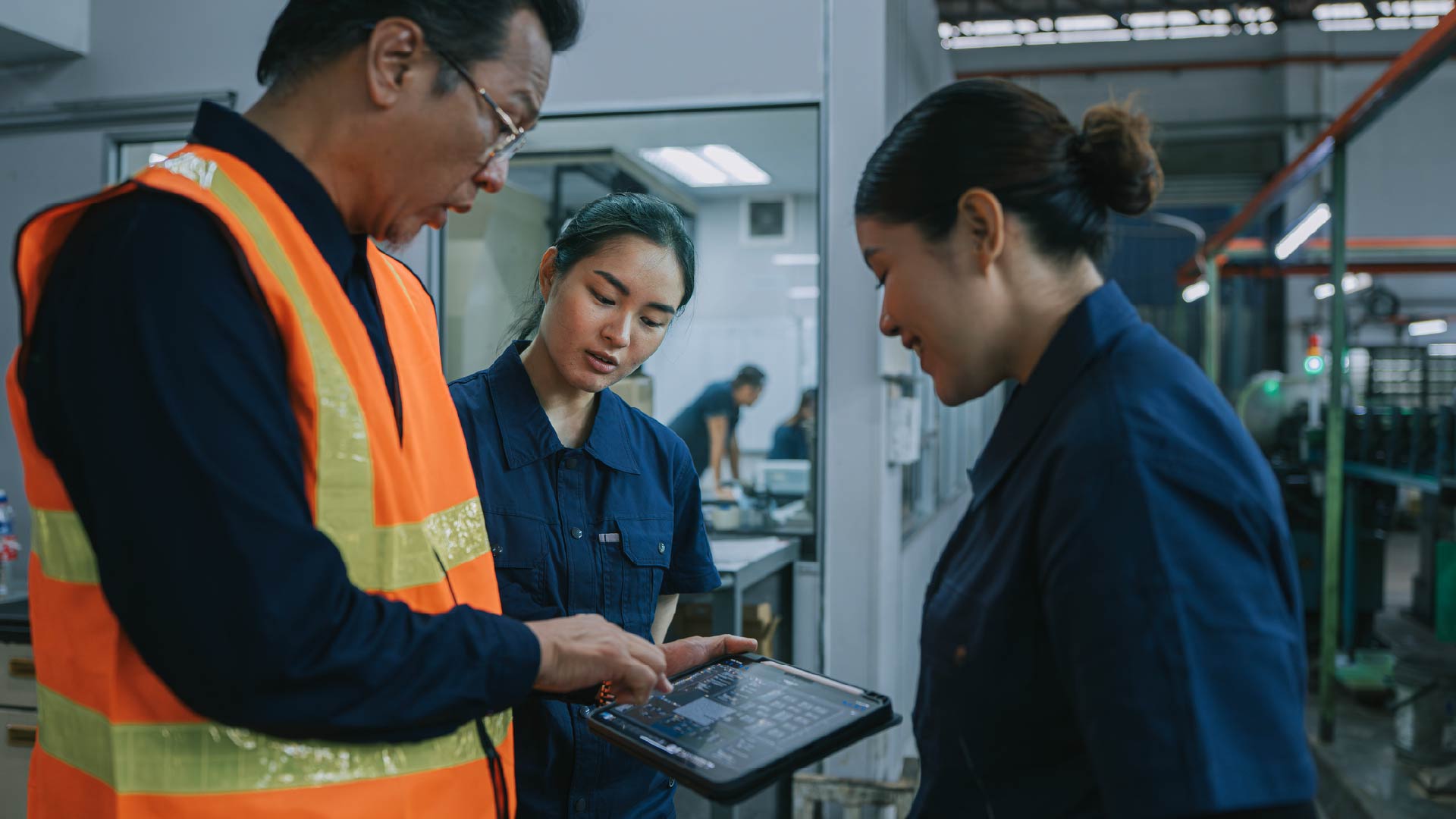
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), commonly found in non-stick cookware, waterproof clothing and food packaging, are facing increased regulation in the US due to their potential to cause harm to human health and the environment. New federal and state regulations aim to address these concerns and mitigate the widespread use of PFAS in daily life. As we enter 2024, significant changes in regulations are poised to revolutionize PFAS management, with far-reaching implications for industries. Organizations must navigate this complex regulatory landscape, to understand the impact on the market.
From January 1, 2024, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has eliminated the de minimis exemption and mandated industry-wide reporting on over 172 PFAS substances added to the Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) list. Reporting requirements now include PFAS in mixtures and exclude simplified Form A reporting. The EPA is also finalizing rulings to designate perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) as hazardous substances under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), while developing new drinking water standards for PFAS under the Safe Drinking Water Act.
Adding to the complexity, states have been implementing their own PFAS regulations, leading to a patchwork of requirements across the country. State regulations vary in terms of permissible PFAS levels, product restrictions and reporting obligations. For example, California requires the labelling of cookware containing PFAS and prohibits the advertising of cookware as PFAS-free if any PFAS are present. Colorado restricts the sale or distribution of products containing intentionally added PFAS from January 2024.
To operate effectively in this complex environment, organizations must stay informed and adapt their practices. Product and chemical compliance software can assist firms in managing supplier data, tracking regulatory changes and ensuring compliance. For example, 3E, a provider of chemical, regulatory and compliance information services, offers 3E Monitor, which aggregates regulatory news and provides actionable insights on regulations. Assent, meanwhile, offers supply chain sustainability software with embedded product compliance capabilities for collecting information, and provides educational content on supplier due diligence, and advisory services.
The new PFAS regulations will reshape the market, requiring industries involved with PFAS-containing products to closely monitor legal developments and comply with evolving requirements. Proactively embracing responsible chemical management practices, and staying ahead of regulatory changes, will position organizations for success in an evolving market.
To learn more about the market for product and chemical compliance, and PFAS requirements, see the Verdantix report Smart Innovators: Product And Chemical Compliance Solutions.
About The Author

April Choy
Industry Analyst