Digital Tools To Shield Workers From Rising Heat Risk In 2024
As global temperatures continue to rise, so too do the risks of heat stress for workers. In 2023, the world experienced its hottest year on record, with temperatures soaring to about 1.48°C above the long-term average before the widespread burning of fossil fuels. This unprecedented warmth, a result of human-induced climate change and a natural El Niño weather event, led to over 200 new daily global temperature records. Focusing on 2024, firms should anticipate similar or even heightened heat risks and must carefully evaluate the protective tools they are utilizing.
In contrast to these urgent climate realities, Texas Governor Greg Abbott controversially approved a law that eliminated local mandates for water breaks for construction workers amidst a week of extreme triple-digit temperatures in 2023. This move disregarded the intensifying consequences of global warming. Texas, known for the highest number of worker deaths due to high temperatures, reported at least 42 workers' deaths from environmental heat exposure from 2011 to 2021, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
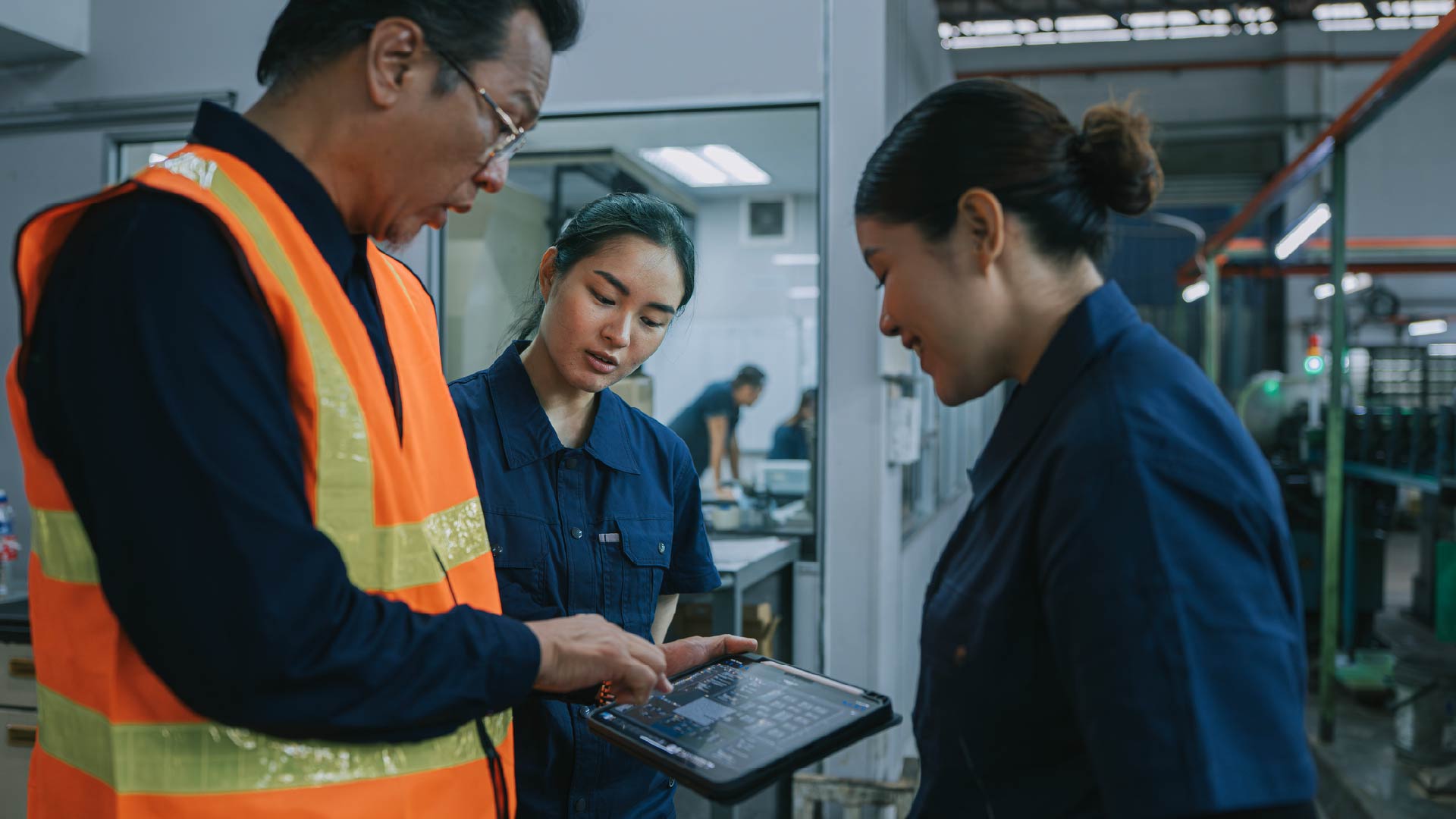
These alarming statistics highlight the urgent need for protective measures against heat-related risks in the workplace, especially as the effects of climate change amplify. In response to this, digital solutions designed to enhance worker safety and productivity in warm environments are emerging to complement traditional strategies such as regular breaks and hydration.
These digital tools tackle challenges posed by workplace heat exposure, which can stem from intense labour, climate-change-induced heat and machinery, resulting in health issues and productivity loss. Innovative solutions include mobile applications providing real-time heat condition insights for informed decision-making and wearable devices with advanced sensors to monitor workers’ physiological responses to heat stress. Such devices enhance safety and ensure regulatory compliance. Furthermore, predictive analytics and IoT-based sensors deliver real-time environmental insights to manage heat risks, while online training platforms provide comprehensive, self-paced heat stress courses, presenting a cost-effective, scalable solution.
As climate change intensifies heat-related workplace illnesses, adopting these digital solutions is critical for enhancing safety, operational efficiency and productivity. To learn more about digital solutions that can mitigate heat risks, read Verdantix Strategic Focus: Digital Tools To Protect Workers From Heat-Related Stress.
About The Author

April Choy
Industry Analyst